Consumer Mobile Application
Kard App
Product Launch
Strategy
What is the Kard Product Launch Strategy and what does it include?
Product launch strategies aim for user adoption and brand growth. How we accomplish these goals will determine the full measure of our success.
Summary
Kard seeks to launch its full suite of Kard branded products within the North America market throughout calendar year 2021, gaining consumer and merchant adoption progressively. We believe that the launch of our products, and our shared success, is solely dependent upon our ability to deliver the unique value created and desired by our customers.
The Kard Product Launch Strategy has been structured to summarize market segments, launch approach, product assessment, product readiness and recommended product enhancements. We recommend that the reader of this document review each section in a linear manner, beginning-to-end, as conclusions are fully informed by the context provided.

Our mission is to drive social commerce and social good through meaningful relationships.
The Kard mission reflects the three core principals of the brand, driving social commerce, social good and meaningful relationships. Our teams have invested considerable time and capital to build a robust platform that centers all consumer and merchant experiences within these focal points.
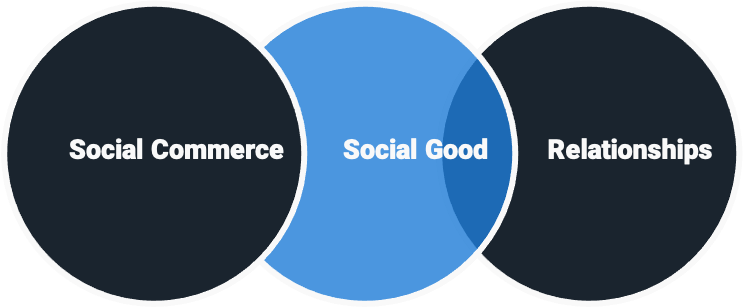
The result of our great effort is a brand that effectively bridges the relationship between consumers and merchants by hosting engaging e-commerce shops, publishing targeted content that appeals to audience-defined interests, promoting discounts/savings and diverse currency offerings.
Glossary
The Kard Product Launch Strategy contains terms that should be properly understood by readers to ensure that the intended scope, distinction and relationships are clear. We will update the glossary periodically as we introduce new concepts and initiatives.
Cashback sevices – A reward platform that pays its members a percentage of money earned when they purchase goods and services via its affiliate links. (Wikipedia)
Closed Loop Card – A closed loop card is an electronic payment card that a cardholder can only use to make purchases from a single company. A closed loop card, also called a single purpose card, will usually have the company’s logo on it, indicating where the card can be used. It may not have the logo of a primary payment processor like Visa or MasterCard, or American Express. Overall, closed loop cards usually require lower processing costs for merchants, which can be one advantage in marketing them to customers, but they do not have as much flexiblity as a traditional debit or credit card. (Investopedia)
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) – Customer relationship management includes the principles, practices, and guidelines an organization follows when interacting with its customers. CRM is often used to refer to technology companies and systems that help manage external interactions with customers. The data-rich platforms serve as a source of information from which engagement campaigns are crafted. (Investopedia)
Fixed POS – A point-of-sale (POS) solution that provides businesses the benefit of a more robust management solution, including enhanced business functionality and inventory management, a cash drawer, employee time clocks, and the capability to manage loyalty programs and gift cards. Fixed POS platforms often extend their functionality to include order management and online ordering functionality. Solutions are traditionally interconnected via local area networks. The software a Fixed POS system runs on can collect valuable information regarding a business that you can analyzed and acted on to improve business operations and business efficiency. (GoCurrency)
Mobile Payments – Generally refers to payment services operated under financial regulation and performed from or via a mobile device.
Mobile POS (mPOS) – A point-of-sale system that performs the same functions as a traditional cash register — except that its operating system is portable. An mPOS system can be integrated with a smart device (tablet or phone). Because a mobile POS system can run off of a smart or digital device connected to the internet, it opens up a world of opportunities for businesses — especially small businesses, street-vendors, and businesses that are typically on the move, such as food trucks. An mPOS terminal allows a business to operate anywhere in the world instead of being tethered to one location like a traditional cash register. The software an mPOS system runs on can collect valuable information regarding a business that you can analyzed and acted on to improve business operations and business efficiency.(GoCurrency)
Online Ordering – The ability to capture and track product orders via the internet, typically initiated from smart devices (tablet and phone). The increase in online ordering has spawned third party food delivery companies that may or may not integrate with a business’s point-of-sale (Fixed or Mobile) platform. Online ordering is offered be leading POS platforms, directly via the business’s web presence, integrated (API) with third party applications and delivery companies with which the business has no established relationship.
Open Look Card – An open loop card is a general-purpose charge card that can be used anywhere that brand of card is accepted. It usually bears the logo of the card brand or network (which processes the actual transactions), such as Visa, MasterCard, American Express, or Discover. In the case of cards offered through financial institutions, like Visas or MasterCards, it often shows the name of the issuing bank or credit union as well. (Investopedia)
Order Management – The ability to track and manage an order (onsite or online) throughout the entire e-commerce journey. Fixed and Mobile POS platforms provide order management by extending functionality from the POS terminal to order preparation staff where they may manage the status of orders.
Point-of-Sale – A system which facilitates the processing and recording of transactions between a company and their consumers, at the time in which goods and/or services are purchased.
Super app – A super app is a closed ecosystem of many apps that people use every day because they offer such a seamless, integrated, contextualized and efficient experience – Mike Lazaridis, BlackBerry
Retail POS Market Overview
Kard competes within several markets, as our platform spans the complete consumer and merchant e-commerce journey. As we intend to compete with each market leader it is important to clearly establish their respective terms, market positions, value and advantage, so that we may best market our brand. Kard competitors offer products and services that are singularly market segment focused, while others combine (integrate) the value of multiple market segments. To date, Kard competitor offerings do not completely align in value scope, as these brands remain segment focused without a singluar core product (super app). As Kard is a “super app” with the combined value of market segment leaders, we must evolve and market our product with a clear focus on segment value.
MarketsandMarkets Analysis 2021
The global retail POS market size is projected to grow from USD 15.8 billion in 2020 to USD 34.4 billion by 2026, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 13.9% during the forecast period. The major growth drivers for the market include growing interest in non-cash transactions among consumers, increased data visibility through cloud POS systems and enhanced service delivery. However, data security concerns may restrain the market growth.
Market Dynamics Driver:
Some of the key benefits of going cashless that are attracting more consumers include safety, growth on saved funds in accounts, better money management, and flexibility. The ability to make different types of digital payments through banking cards is enabling consumers to opt for cashless payment modes. Users can store their card information in digital payment apps or mobile wallets to make cashless payments. With the rising concerns over the safety of handling cash transactions due to the COVID-19 pandemic, merchants, as well as consumers, are relying on contactless payment modes to avoid the risk of getting infected.
Restraint: Data security concerns
Retail POS systems are prone to security vulnerabilities, such as device faults, skimming, phishing, and software and network weakness. Owing to the unsecured networks, hackers can easily infiltrate the infrastructure and access valuable records, such as business account data and customer credit card details. Even if the network is well-protected, devices need to be secured too. Hence, selecting technology products with inherent security measures is critical when deploying POS devices. With more advanced technologies being deployed and the growing integrations between the enterprise system, there is a significant rise in threats, such as data thefts and cyberattacks.
Opportunity: Growing interest in POS solutions among small businesses
Small businesses are implementing POS systems to benefit from the host of benefits associated with them. Effective POS systems allow business owners to reduce time spent on business/store administration by offering relevant reports to help speed-up decision-making, in a timely fashion. The streamlined POS systems also aid in increasing store profitability through effective inventory management. Solutions also facilitate targeted and personalized marketing campaigns through customer data acquired during sales transactions. As small businesses struggle with managing capital expenses, reports produced from POS data can offer a bird’s eye view of the business operations to determine the efficiency of different departments.
Challenge: High maintenance cost of wireless POS systems
The maintenance cost associated with the wireless POS systems is very high. Fixing the hardware used in POS systems is a difficult task. Despite being able to contact the manufacturer to help the user troubleshoot the problem, it may still require a costly, time-consuming visit from a service provider to fix the problem. Unlike the web-based systems providing free upgrades that keep them updated, the software-based upgrades cost too high. As a part of business expansion, every time an upgrade is necessary, the user has to pay for new licenses and software. The monthly subscription charges associated with these systems may diminish the Return on Investment (RoI) in the long run.
Grocery stores segment to hold the largest market size during the forecast period
Grocery stores have some tough competition and large chain supermarkets use technology to make their jobs easier. A POS system helps manage the grocery stores and makes checkouts quicker. The grocery store software will help better organize the business and meet customer expectations. For instance, National Retail Solutions created the POS+ so that hard-working businesses can have the same opportunities as bigger grocery stores and it offers countless advantages. Independent stores, such as small shops, present at a single location are highly adopting retail POS terminals for providing customers with digital payment services.
Mobile POS Market Overview
The global mobile POS (mPOS) terminals market size is expected to reach USD 42.99 billion by 2022, according to a new study by Grand View Research, Inc. Mobile POS terminals have evolved from basic payment processing tools to advanced analytics solution providers with greater processing capability and wireless communication support. The inflection of these terminals came with the adoption of consumer grade devices such as tablets for business use. Ubiquitous wireless connectivity such as the Bluetooth, availability of mobile printers, scanners, card readers and peripheral devices; and multiple platform support have driven the mobile POS terminals market in various applications.
Sophisticated data analytics, growing credit card payments and ever-changing consumer expectations are expected to spur the mobile POS terminals industry. This growth has encouraged retailers to leverage new applications and strategies to deliver seamless customer experience. Mobile applications have the ability to create new channels for revenue growth; as a result, vendors are increasingly trying to understand various marketing channels available in order to leverage technology to compete. Flexibility of having a tablet-based mobile POS owing to low installation costs has attracted SMBs to invest in this technology. Reduced customer time in line, increased security, free floor space and paper-free receipting services are the features driving mPOS terminals demand over traditional or fixed terminals.
The growing penetration of tablet devices, rising base of SMBs and micro-merchants, need for effective line-busting schemes to encourage card adoption are expected to propel market growth over the coming years. However, lack of standardization and data security concerns may restrain mobile POS terminals market growth. Increased penetration of Near Field Communication (NFC) in mobile devices is expected to augment demand. (Grand View Research)
E-Commerce Software & Platform Market Overview
E-commerce software and platforms provide an effective solution for digital commerce enabled businesses. The main features of e-commerce software and platforms are shopping cart software, shopping cart solution, online store builder, e-commerce website builder and others. Apart from this, e-commerce software and platforms operate with an integrated shopping cart, search engine optimization (SEO), email marketing, analytics and others.
The global e-commerce software and platform market is expected to expand at a robust Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) over the forecast period i.e. 2018-2027. Factors such as high disposable income coupled with growth in consumer spending on clothing is anticipated to increase the growth of the global ecommerce software and platform market. Moreover, the ecommerce industry has grown remarkably well in the previous years and is likely to witness exponential growth in the upcoming years.
The market is segmented in five major regions including North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Middle East & Africa and Latin America regions. Among these regions, Asia Pacific is projected to dominate the overall ecommerce software and platform market. Rise in the number of business establishments is providing many opportunities for e-commerce software & platform service providers. This factor is expected to positively impact the growth of the e-commerce software and platform market over the forecast period.
The North America e-commerce software and platform market is poised to grow at a poised rate over the upcoming years. The rising number of startup establishments across the region is fostering the growth of the global ecommerce software and platform market. The European region is expected to observe outstanding growth in the upcoming years. Increasing consumer spending and the increasing number of e-shoppers is anticipated to drive the growth of the global ecommerce software and platform market over the upcoming years.
Based on software & platform type, e-commerce software and platform market is segmented into, commerce, order management, business intelligence, shipping and others, out of which, commerce is accounted for the largest market share in overall global ecommerce software and platform market over the forecast period. (Research Nester)
Mobile Payments Market Overview
The global mobile payments market is anticipated to grow significantly over the forecast period. Mobile payments refer to payments or transactions made under financial supervision by regulatory bodies using a mobile device. This service does away with traditional alternatives such as credit cards, checks, and cash, providing a high degree of ease to end users.
Payments can be made by using apps such as Square Wallet which must be installed on the customer’s phone, and which need to be linked to their financial credentials. Alternatively, near field communication or NFC technology can be used, wherein the user’s phone needs to be tapped against the NFC enabled point-of-sale (POS) terminal. In order to use this method, apps such as Isis or Google Wallet need to be used, and the user’s phone needs to be NFC enabled. Besides financial cards, loyalty cards, and other coupons can be integrated into the device, making for enriched user experience.
The Growing propensity to use smartphones and increasing penetration of mobility and smartphones, especially in emerging nations, is expected to fuel market growth. The advent of budget mobile phones that are capable of supporting mobile payments has also spurred overall demand. Since users do not need to rely on traditional modes of payment and can conduct payment as well as remittance services using a consolidated device, this technology has helped bridge the gap between the banked and underbanked population to a large extent. As a result, it has received favorable initiatives by organizations and regulatory bodies, since it is particularly useful in regions with low bank penetration. Security concerns among users are expected to restrain the market. Furthermore, the loss of the mobile device configured with financial details is a credible concern. However, service providers are equipped for dealing with such issues, and can remotely suspend the user’s account, thus safeguarding the mobile wallet.
The EMEA region accounted for the largest market share in 2012 on account of technological advancements in Europe along with the presence of the underbanked population in Africa. Asia Pacific is expected to be a fast-growing market segment over the forecast period. Key market participants are divided into their offerings; they include Google, Apple Inc., Samsung, American Express, Visa, Amazon, PayPal, etc. (Grand View Research)
Core Value Services
___________
mPOS
E-Commerce
Payments
Merchant Services
CRM/Marketing
Social Engagement

Product Launch Approach
“It is critical to design a process that allows you to launch vastly different product experiences within specific communities so your product can reach critical mass.” – Founders, To Be Honest (TBH)
The recommended product launch approach for Kard is to employ a Repeatable Launch Process (RLP), first defining then evolving target audiences and market segments, validating assumptions or hypothesis regarding product value through feedback, and iteratively enhancing Kard product value to ensure adoption and promotion of our products. The ultimate goal of the RLP is to efficiently and effectively gather and act upon information (feedback) provided by product users (Product Champions) that represent our best-defined market segment.
Our initial RLP step is to narrowly define a target audience segment, focusing on the most viable, engaged and influential Kard App Consumers. Contrary to traditional models that blanket large geographic markets with moderately nuanced messaging, the RLP seeks to first reach the ideal customer. The most apparent benefit of the recommended approach is a greater potential for qualitative and quantitive feedback from ideal customers.
An RLP may only be successful if all core aspects of Kard (organization) are committed to each step of the related cycles. Kard Product Management and Engineering teams must be poised to quickly respond to design and functional challenges or recommendations.
Benefits
The Repeatable Launch Process (RLP) is designed to yield the most valuable input from hyper-targeted Kard App Users. Our ability to quickly and effectively evolve the Kard App product throughout this progressive launch process is guided by a well-structured launch team comprised of Product Management, Engineering, Marketing, Sales, Operations & Compliance leaders. Kard must ensure that the RLP, the availability team leaders and their respective priorities are align. If properly employed Kard should strive to achive the following benefits:
-
- Target market segment audiences that best represents the ideal Kard product user
- Target market geographic audience segments that best represent ideal Kard product users
- An engagement model that may be rapidly employed for product evolution, feedback and guidance
- Target market segment audience profiles that can guide the creation and execution of effective marketing campaigns
Repeatable Launch Process Steps
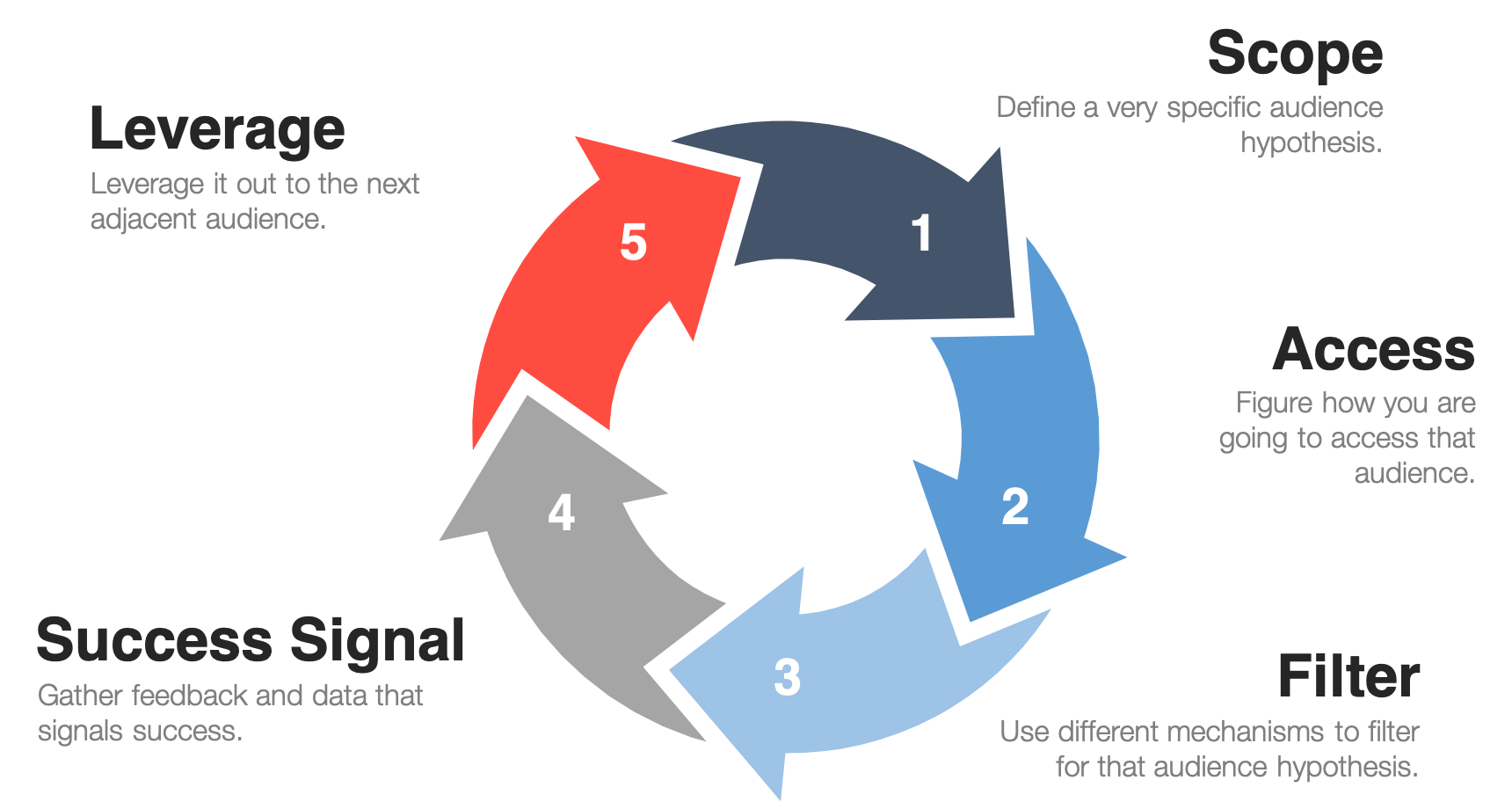
The Repeatable Launch Process (RLP) outlines core steps that best position Kard to yield the aforementioned desired results. We must properly align our effort with each of the noted steps.
Define Scope – Start by defining our target audience. Instead of blasting our entire audience with Kard products or features, we should use product development to build products and features for specific audiences. This requires narrowing down our target audience within our user base as much as possible. Although Kard has not formally launched within the North America market, our market segment competitors have established and published profiles that should align with our brands. The defined scope of Kard App Users must consider the following attributes:
-
- Age
- Gender
- Income
- Education
- Marital Status
- Buying Habits/Behavior
- Interests
- Geography
- Population Density
- Community Type (Suburban, Metropolitan etc.)
Access – Get in front of these people. Use tactics like email, paid ads, press releases, or social media to announce product changes and referrals to promote Kard products or feature to our audience. As the Kard Sales team has a well-established network of geographically diverse markets, we may rely upon these relationships to engage target audiences. We may also consider establishing groups of Product Champions within their respective geographic areas. Champion groups must be formally engaged, clearly articulating our process and shared goals, the benefit of engagement, the time required for participation and feedback mechanisms.
Filter – Once we have our audience’s attention, find the users most likely to appreciate and understand the beta version of our product or feature. Who are our early adopters? Sharing our launch with target groups is a little like casting a net. We’re going to find some people who fit the scope we’ve defined, and others who aren’t an exact fit. Filtering helps us get to the right audience.
Success Signals – Narrowing our target audience makes it easier to earn success signals, as opposed to targeting everyone at once. The results are more accurate, less noisy qualitative and quantitative signals that give a stronger indication of whether we’ve achieved product/market fit. If we’re launching a feature inside a larger product, we should go one step further to find feature/product fit. Without feature/product fit, we end up with lots of new features but no lift to retained users. Our success signals should be an objective and measurable value, whereas we encourage the Kard App Champion to apply a weighted metric as feedback. Once completed, we may quickly calculate the aggregate value of feedback and leverage this information for future enhancements.
Leverage – The final step of the RLP loop, once the success signals have been identified, is to figure out how to leverage these signals and launch to the next group of defined target users. We should expose Kard App features to more users progressively over time as more value is added to the product with each iteration.
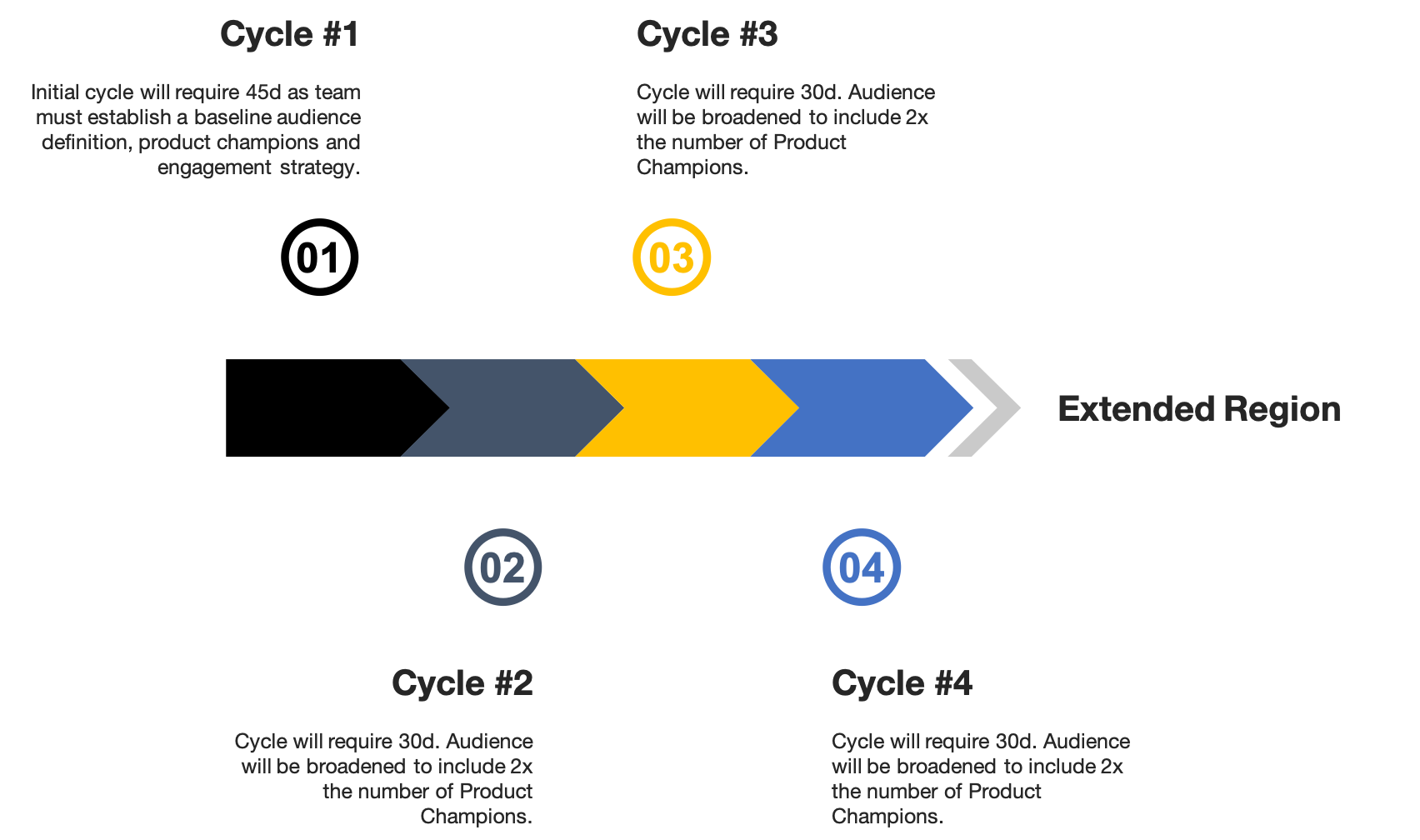
Repeatable Launch Process Timeline
Kard App Assessment
“We believe that our products will be embraced by market segment value, as opposed to the “super app” moniker.
We have invested considerable time and resources in the design and subsequent development of the super app, Kard. Super apps aren’t new. Asia, China and Latin America market shave broadly embraced these platforms. Many have undoubtedly heard of them before. The surge of those umbrella apps encompassing a wide range of services is a deep-rooted trend in emerging countries, conquering Southeast Asia as well as Latin America. In those regions, super apps are a lifestyle. As previously discussed, Kard’s product positioning as a super app must be built upon delivering value across multiple market segments, specificallly e-commerce, cashback, payments, merchant services, crm/marketing and social engagement.
We believe that our products will be embraced by market segment value, as opposed to the “super app” moniker. It is this belief that compels us to solve market segment challenges first, then encourage subscribers to leverage the value of related Kard features. Our assessment of Kard product market segment value is quite objective, considering apps that exist in the current market place. Assessment criteria have been established to best determine if/when such value may be leveraged successfully and the related user experience. The following focal points (criteria) best reflect our effort to assess Kard products. We have applied these criteria to each of the noted market segments.
E-Commerce
Competitors – DoorDash, Uber Eats, Grubhub, Postmates
Kard App E-Commerce Competitive Assessment – Kard e-commerce processes and assets, although not competitively positioned, may be included in the Soft Launch. Its inclusion in the Kard Repeatable Launch Process (RLP) must be aligned with the recommended enhancements.
Kard App E-Commerce Summary – Kard App is not currently positioned to faciliate the complete e-commerce journey, as consumers may only identify opportunities to save and earn CashBack (100+ merchants supported), without the ability to browse and purchase merchant products and services in-app. Although Kard has secured relationships with third-party coupon, gift card and discount providers, the e-commerce journey may not be completed as we have neither integrated with merchant point-of-sale (POS) systems nor established a Kard Business subscriber base within the North America market. Given the state of Kard’s e-commerce journey capabilities our initial tagline “Shop, Save and Earn” must be revised due to the lack of full e-commerce journey capabilities, replaced by “Pay, Save and Earn” until platform enhancements are completed. The shift in tagline, a direct reflection of the current platform capabilities, negatively impacts Kard’s market segment (e-commerce marketplace) positioning.
Competitors within the e-commerce food delivery market segment (DoorDash, User Eats, Grubhub and Postmates) offer a significantly broad listing of merchants from which consumers may browse and ultimately complete purchases. Kard is currently advancing strategic relationships with leading POS systems manufacturers and partners to yield integration sufficient enough to retrieve merchant product catalogs, menus, a Kard payment option and merchant services. Upon securing such strategic agreements Kard will be able to effectively build its merchant marketplace. The noted strategic goals may be achieved throughout the 2021 calendar year, although adoption by merchants will be a lengthy process.
We have recently reviewed an alternative e-commerce experience that will empower Kard to facilitate the full e-commerce journey in-app, while offering the consumer the ability to realize published savings. Further, the alternative approach will allow Kard to advance the usage of its Cash Kard, gift cards and related merchant services, without the requisite POS integration. Should we adopt the proposed concept Kard may also secure more profitable independent affiliate agreements with merchants. Further details are available upon demand.
CashBack
Competitors – Rakuten, Ibotta, Honey, CapitalOne Shopping
Kard App CashBack Competitive Assessment – Kard CashBack processes and assets, although not competitively positioned, may be included in the Soft Launch. Its inclusion in the Kard Repeatable Launch Process (RLP) must be aligned with the recommended enhancements.
Kard App CashBack Summary – Kard App provides consumers with the ability to identify opportunities to save on purchases via Entertainment.com and Incomm (100+ merchants supported). When assessed singularly is modestly competitive. The range of suppored retailers by competitors is as follows:
-
- Honey – 30,000
- Capitalone Shopping – 30,000
- Rakuten – 2500
- Ibotta – 300+
We have recently reviewed an alternative e-commerce experience that will empower Kard to facilitate the full e-commerce journey in-app, while offering the consumer the ability to realize published savings. Further, the alternative approach will allow Kard to advance the usage of its Cash Kard, gift cards and related merchant services, without the requisite POS integration. Should we adopt the proposed concept Kard may also secure more profitable independent affiliate agreements with merchants. Further details are available upon demand.
Payments
Competitors – PayPal, Square (Cash App), Venmo
Kard App Payments and Social Engagement Competitive Assessments – The Kard App Payments processes and assets are competitively positioned and should be included in the Soft Launch and Kard Repeatable Launch Process (RLP)
User Experience
Kard App Invitation Competitive Assessment – The Kard App Invitation process and assets, although not competitively positioned, may be included in the Soft Launch. Its inclusion in the Kard Repeatable Launch Process (RLP) must be aligned with the recommended enhancements.
Kard App Invitation Summary – The Kard App Invitation to join is a mobile app user’s first experience with our brand. The primary goals of this initial engagement must be to establish our brand’s personality and to compel the potential subscriber to provide only the information required to begin building a formal relationship. Unclear directions, poorly structured UI and Call to Action (CTA) will create confusion and increase registration abandonment.
Kard employs a grey user approach to subscriber invitations whereas the initial request is aligned with a mobile phone number and the potential user must claim the Kard account. Kard App Invitations may be received via email or text, instructing the potential user to “sign up” and subsequently earn a “bonus”. All invitations are structured with a single paragraph, followed by the mobile phone number and email address of the Inviter. The CTA is the full unique URL with a Reference ID. Upon engaging/selecting the URL an Invitee’s browser is opened and they are directed to a long-form registration page. Kard requires new subscribers to complete the full registration process first, an unnecessary practice that increases the abandonment rate. Future Kard App enhancements should include the following recommendations:
-
- HTML enabled
- Summary of the registration process
- CTA button
- URL labels only
- Brand logo
- Brand value statement
- An in-app process that collects the information necessary to begin full brand engagement, specifically name (first and last), email address, password and PIN. Additional information (e.g. address) will be collected upon selecting a subscription package. The recommended process will immerse the registrant in the brand experience much faster.
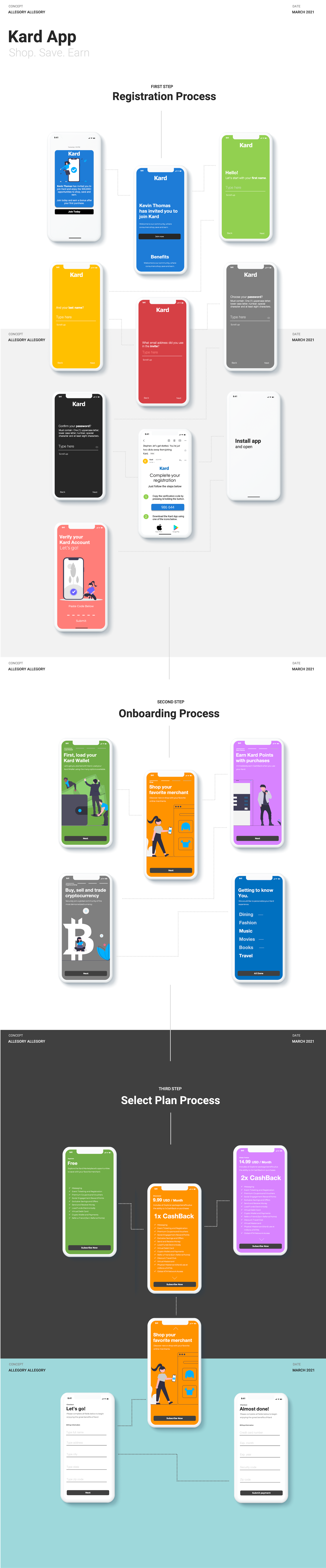
Current Invitation and Invitation Concept
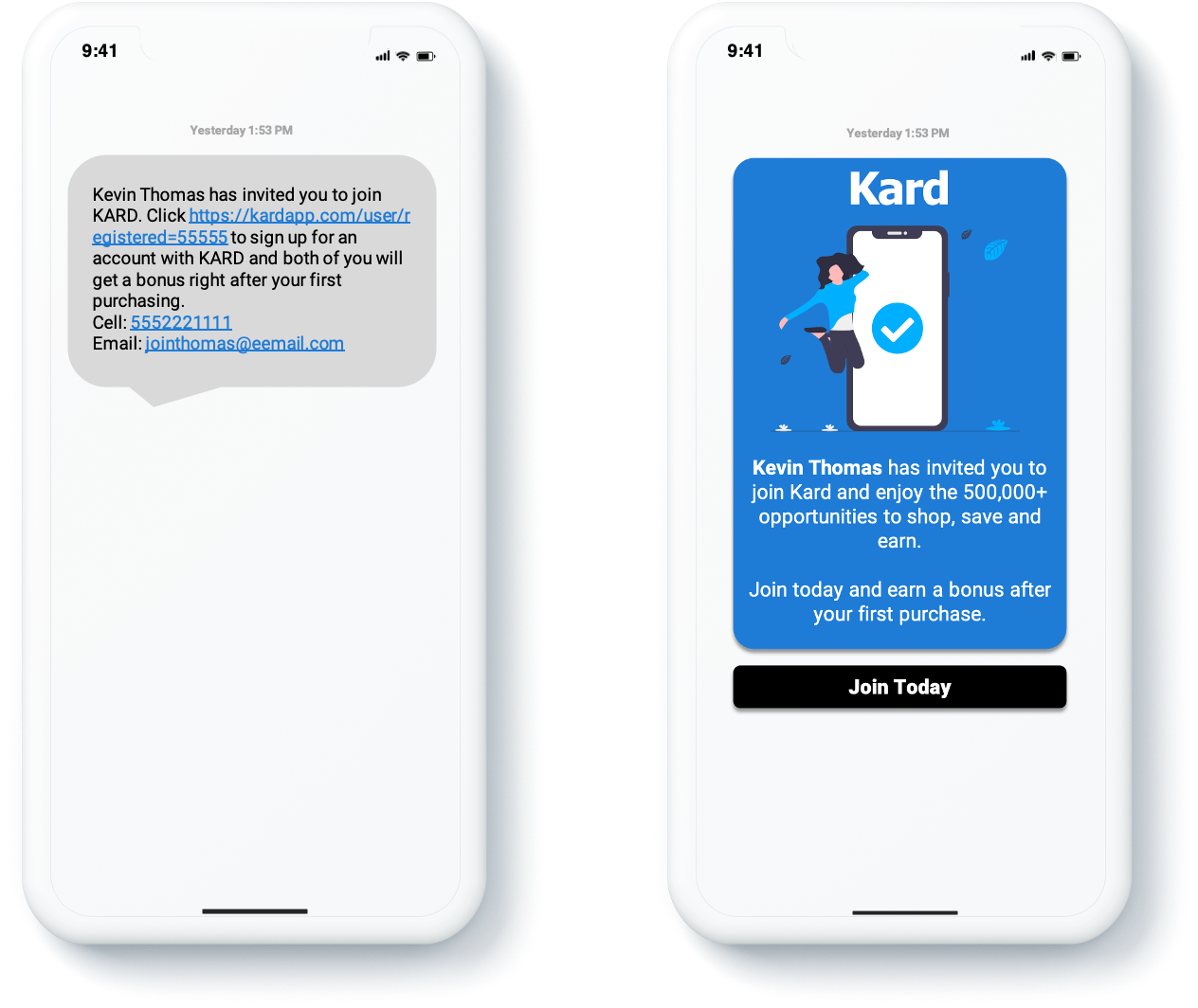
Kard App Registration Competitive Assessment – The Kard App Registration process and assets, although not competitively positioned, may be included in the Soft Launch. Its inclusion in the Kard Repeatable Launch Process (RLP) must be aligned with the recommended enhancements.
Kard App Registration – Kard employs three unique registration experiences:
-
- Referral link registration – Invitee selects referral link which initiates web browser registration process
- Direct web registration – Registration is completed using a web browser
- Mobile registration – Registration is completed from mobile app (unclear)
All registration flows require that registrants use the same email address to log into the mobile app upon download, binding the app to the account once completed. The current binding scheme relies upon user compliance to ensure creating a successful link between the platform account and the mobile app. It is worth noting that alternative methods of binding have been broadly adopted by competitors, utilizing verification codes created after referral and direct web registration. The noted method mitigates the risk associated with the registrant using an unrelated email address to bind their account. Future Kard App enhancements should include the following recommendations:
-
- Streamline registration UI flow – A modern in-app registration process
- Account verification UI flow – A modern in-app binding process
Registration Concept
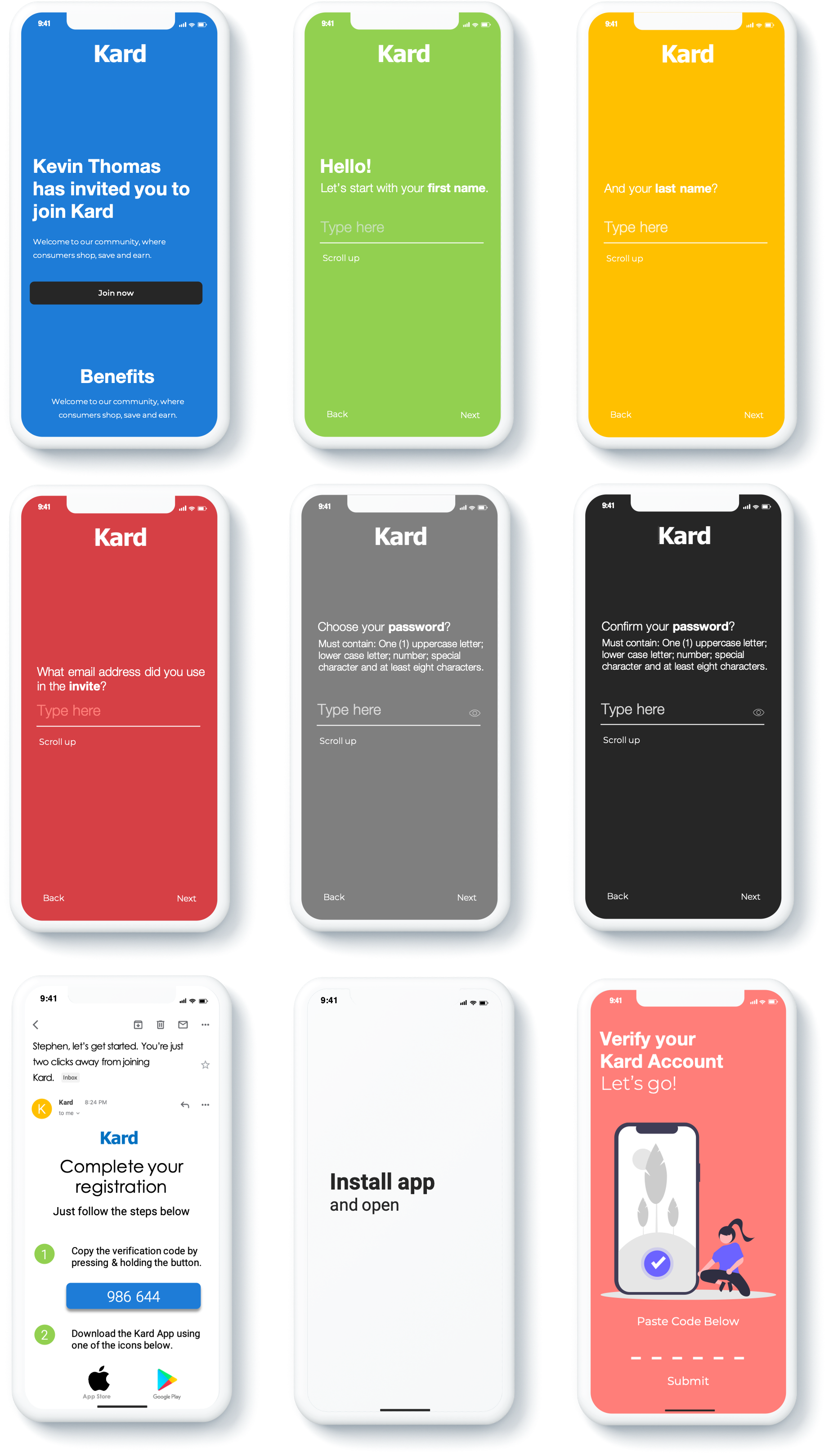
Kard App Onboarding Competitive Assessment – The Kard App Onboarding process and assets, although not competitively positioned, may be included in the Soft Launch. Its inclusion in the Kard Repeatable Launch Process (RLP) must be aligned with the recommended enhancements.
Kard App Onboarding Summary – Kard App does not employ an in-app onboarding experience for new subscribers. To date, Kard has developed a series of onboarding assets and frequently asked questions (FAQs) that may be accessed after registration, however, new subscribers are not directed to engage these materials to best familiarize them with the Kard brand and value. Many of our competitors have adopted onboarding processes that immediately guide new subscribers through related key features and product value, thus enhancing the rates of adoption and continued usage. Future Kard App enhancements should include the following recommendations:
-
- In-app onboarding series – A modern in-app onboarding flow that highlights key features and compels users to load funds, shop with their favorite merchants and save.
- Post registration onboarding – Email series that progressively guides new subscribers through Kard features and value.
Onboarding Concept

Conclusion
“Driving social commerce and social good through meaningful relationsips
Reference Illustrations
The provided illustration captures the recommended complete process flows for Invitation to Join, Registration and Onboarding.